Bloomberg's Leah Nylen reported Thursday that "a Colorado judge issued an order temporarily blocking the proposed $25 billion merger of Kroger Co. and Albertsons Cos., which has been challenged by…
Fertilizer Prices Continue to Climb, 2022 Planted Acreage Analysis Continues
DTN writer Russ Quinn reported last week that, “Nitrogen fertilizers maintained their spot as the clear leaders as average retail fertilizer prices continued to climb higher the fourth week of November 2021, according to sellers surveyed by DTN.

“Seven of the eight major fertilizers recorded considerable moves higher compared to last month. DTN designates a significant move as anything 5% or more.
Leading the way higher was anhydrous, which was up a mammoth 33% from a month prior. The nitrogen fertilizer’s average price was $1,308 per ton, which continues to be all-time high in the DTN data set.
Mr. Quinn noted that, “UAN32 was 26% more expensive compared to last month with the average price at $660/ton, an all-time high. UAN28 was 25% higher compared to last month with the average price of $574/ton, also an all-time high.
“Urea was 16% more expensive compared to last month with an average price of $868/ton. This is also an all-time high in our data. 10-34-0 was 14% more expense looking back to last month with an average price of $755/ton.”
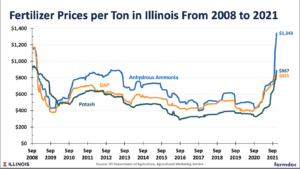
Fertilizer prices have been climbing since early October.

And in an update earlier this month from CoBank, “Fertilizer Inflation Likely to Persist into Spring Planting,” Kenneth Scott Zuckerberg stated that, “Recent talk suggests that U.S. farmers will plant more soybeans and less corn in 2022 due to rising fertilizer prices. While technically true compared to 2021 (i.e., that soybean acres will rise nominally and corn acres will fall nominally relative to each crop’s actual planted acres in 2021), we do NOT see a crop mix scenario of higher soybean acres over corn in absolute terms for a few reasons.

“We expect U.S. ethanol producers’ demand for corn to remain strong amidst current high fuel prices and record blending margins, and we expect a slowdown in soybean sales to China. USDA’s November 5 acreage baseline update aligns with this, forecasting 92.0 million corn acres versus 87.5 million soybean acres for the 2022-23 crop year. Although corn acreage is forecast to drop 1.3 million acres, this is primarily due to increased acres for wheat and cotton, both of which are currently at or near record-high price levels.
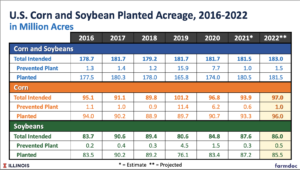
In Monday’s farmdoc webinar, @ScottIrwinUI provided a look at total intended planted acreage projections for 2022 by using the previous year’s #corn price as an analysis variable (clip, two minutes). pic.twitter.com/qcov1eyfAs
— Farm Policy (@FarmPolicy) November 30, 2021
“Given the above, the current price ratio of soybeans to corn, admittedly a simple tool, shows that soybean prices are currently quite weak relative to corn. At present, soybean prices are only 214% of corn prices, compared to a long-term average of 253% . According to USDA, higher price ratios indicate that soybeans are relatively more profitable than corn, while lower ratios indicate the opposite and thus support greater planting of corn.”
During Monday’s farmdoc webinar, @ScottIrwinUI projected combined planted acreage of #corn and #soybeans at 181.5 million acres in 2022 (clip, 90 seconds). pic.twitter.com/IXZ7PW51F7
— Farm Policy (@FarmPolicy) November 30, 2021
The CoBank report added that, “Over the next six months, CoBank believes there is a high probability that fertilizer prices will remain elevated against a backdrop of record general inflation, above- average natural gas prices, tight global nitrogen supplies and continued strong farmer demand.
After projecting 181.5 million combined planted acres of #corn & #soybeans in 2022, @ScottIrwinUI used a break-even futures base ratio of 2.3 & projected 96 million acres of planted corn and 85.5 million acres of planted soybeans for 2022 in Monday's webinar (clip, 2 minutes). pic.twitter.com/d16zoxR6aA
— Farm Policy (@FarmPolicy) November 30, 2021
“Further, we do not forecast that soybean acres will exceed corn acres due to high nitrogen-based fertilizer prices, although that will likely change in the longer term as biofuel production leans more towards soybeans (for use in renewable diesel) versus corn (used in ethanol).
“Finally, in contrast to the 2008 to 2010 period, farm supply cooperatives appear more focused on managing the risk of write- downs of fertilizer inventories should a rapid drop in prices occur.”





