As a result of the attack on Iran, nitrogen fertilizer at the port of New Orleans has seen an increase in price this week. Urea prices for barges in New…
CoBank, University of Missouri Report: “The Importance of Off-Farm Income to the Agricultural Economy”
CoBank’s Knowledge Exchange division, in partnership with the University of Missouri, released a report yesterday titled, “The Importance of Off-Farm Income to the Agricultural Economy.” Today’s update includes highlights from the report, which was written by Alan Spell, Keri Jacobs, Sarah Low, and Justin Krohn.
The report pointed out that, “Jobs in other industries are vital to farm households, as half of these households have negative farm income in a typical year. Most farmers (70%+) cited reliable income as the top reason for off-farm jobs in a 2018 survey. Stable income was especially important for small family farms, the vast majority (92%) of all farms.”
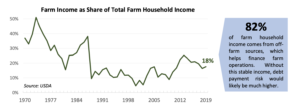
More narrowly, the report noted that:
- Most principal operators (56%) had a main job off the farm in 2017, compared to 37% in 1974.
- Low debt-to-asset ratios for a farm household suggest reduced financial risks. From 2011-2019, so-called off-farm occupation farms averaged 6.3% debt-to asset ratios. For midsized-to-larger farms, where operators typically do not work off-farm, the ratio averaged over 13 percent.
- A Kansas City Federal Reserve study suggested that agricultural producers in rural counties with weak labor markets had higher debt repayment risks, because of fewer off-farm job opportunities.
The University of Missouri authors pointed out that, “Young and beginning farmers are more likely than other farmers to have a primary job off the farm. Off- farm income is critical for lowering debt risks as these farmers build their businesses.
- Nearly 2 out of 3 younger operators (63%) had a primary off-farm job in 2017, compared to 56% of all principal operators.
- Debt-to-asset ratio analysis and other research shows that off-farm jobs reduce financial risks, especially important for younger farmers who face higher debt needs as they grow their business.
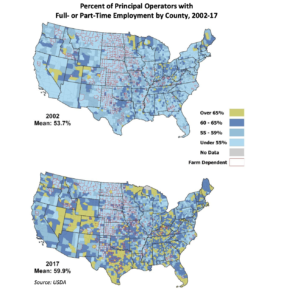
With respect to the occupations of off-farm employment, the CoBank – University of Missouri update indicated that, “Exhibit 15 [below] shows the 2018 off-farm occupations, or job positions, identified by principal operators and their spouses. The majority of off-farm occupations were in Management & Professional or Natural Resources, Construction & Maintenance positions.”
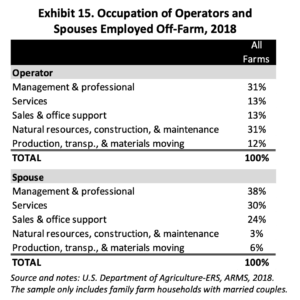
“Management & Professional positions were also top occupations for spouses in 2018, followed by Services-related jobs.”
Adding perspective to the issue of why agricultural operators have an off-farm job, yesterday’s report stated that, “All households, regardless of farm size, indicated the main reason was that off-farm income was more reliable than farm income (70% or more).

“50% or more of all households replied that it was more lucrative. Health and retirement benefits were also a reason for over half of all farm households. Stable income, and related health care and retirement benefits, were especially important for small family farms, the vast majority (92%) of all farms.”





